Projects
This portfolio showcases a range of projects, from AI-driven surgical video recognition to predictive biomarkers to the start of my research journey in geriatrics. Through this page, I aim to share the insights gained from my research and discuss innovative solutions in advancing patient care.
Urine Concentrations of Prostate-Specific Extracellular Vesicles for Pre-Biopsy Prediction of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Fabrice Lucien
In this study, we developed a new method to improve the accuracy of detecting aggressive prostate cancer using prostate-derived extracellular vesicles (ProsEVs) found in urine. Our predictive model demonstrated a high level of accuracy in identifying clinically significant prostate cancer while reducing the risk of unnecessary biopsies and overdiagnosis. This non-invasive test has the potential to revolutionize prostate cancer screening, leading to earlier detection of dangerous tumors and sparing many men from unneeded procedures. We are excited to further refine and validate this promising technology to improve outcomes for prostate cancer patients worldwide.
First Author Manuscript under review
.png)
B7-H3 as a Predictive Biomarker for Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Fabrice Lucien
In this study, we investigated the potential of B7-H3, an immune checkpoint molecule, as a predictive biomarker for pathologic response to neoadjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients. Our findings suggest that high B7-H3 expression in pre-treatment bladder biopsies is associated with a lower likelihood of achieving pathologic complete response, highlighting its potential role in chemotherapy resistance.
.png)
Changes in Body Composition Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Vidit Sharma
This study investigated the impact of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) on body composition and post-operative complications in bladder cancer patients undergoing radical cystectomy. We found that NAC was associated with significant declines in skeletal muscle index and progression to sarcopenic obesity. These findings highlight the potential of using AI-derived body composition measures to individualize pre-operative patient counseling and risk assessment.
First Author Manuscript under works.

Automated Detection and Classification of Surgical Tools: Potential for Improved Surgical Safety using Artificial Intelligence
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Abhinav Khanna
In my project, I developed an AI-based computer vision model that can automatically detect and count surgical tools during surgery. The model was trained on a dataset of over 13,000 surgical tools across 11 categories and showed high accuracy in distinguishing tools from the background and differentiating between various tool types, even when tools were overlapping. When tested on a real-time surgical video, the model maintained a correct count of surgical tools and processed the video at a speed of around 40 frames per second. This AI safeguard has the potential to improve patient safety by preventing retained surgical items and reducing the manual workload on surgical staff.
Link to First Author publication

Real-Time Kidney Stone Segmentation During Distinct Ureteroscopic Tasks Using a Computer Vision Model
Vanderbilt University
PI: Dr Nicholas L Kavoussi
This study developed a robust deep learning model for automated kidney stone segmentation in ureteroscopic videos, trained on a large dataset of diverse cases. The model demonstrated excellent performance across various surgical tasks and endoscopic modalities, with non-inferior segmentation accuracy compared to expert endourologists. This foundational work establishes the feasibility of real-time operative video annotation and represents a crucial step towards developing an image-guided surgical system to improve patient outcomes in ureteroscopic lithotripsy.
Manuscript under submission.

Predicting Pathologic Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Using Pathology AI
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Abhinav Khanna
In this retrospective project we are using TURBT slides of patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy to find subvisual features on pathology slides using computer vision based algorithms to improve prediction of response to NAC.
Determination of Split Renal Function from CT Imaging
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Abhinav Khanna
In this project, we are leveraging a cohort of over 900 patients with both CT imaging and a Nuclear medicine and by building upon a prior model designed to segment the kidneys from renal imaging, to extract radiomics data in addition to volumetric and clinical data to create a model that can predict CT split renal function non-inferiorly to the nuclear medicine scan. This would be valuable given the logistics challenges of scheduling two tests along side the additional ~$1000 cost of a nuclear medicine scan of the kidneys.

Comparing Frailty Indices for Risk Stratification in Urologic Surgery: Which Index to Choose?
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Abhinav Khanna
Frailty has become a very commonly referred to metric but there has been little comparison between frailty indices. In this study, I compared the predictive ability of two commonly used frailty indices, the revised-RAI, and the mFI. Using data from the NSQIP database, I performed multivariable logistic regression analyses to investigate the association of these frailty indices with various post-operative outcomes. The results showed that the revised-RAI generally had higher discriminatory ability for outcomes.

Evaluating the Impact of Artificial Intelligence-Based Assessment of Body Composition on Primary Artificial Urinary Sphincter Placement Outcomes
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Brian Linder
This study investigated the impact of sarcopenia, characterized by muscle mass loss, on artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) device outcomes in men with post-prostatectomy incontinence. Although sarcopenia was prevalent among AUS patients, it did not significantly impact overall device survival, suggesting that AUS placement may be safe in well-selected sarcopenic patients, despite an increased risk of device infection.
Link to Manuscript
Link to AUA North Central Section abstract

Inpatient Gross Hematuria: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Resource Utilization: Results from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Vidit Sharma
This study analyzes inpatient gross hematuria (GH) using data from 2016 to 2020, revealing an increasing incidence from 0.41% to 0.50%. Key findings include higher GH prevalence in males, older patients, and those with histories of radiation or anticoagulation use. Over half of the GH cases occurred outside of urology, particularly in cardiovascular, infectious, and respiratory admissions. GH patients required more medical interventions and incurred higher hospital charges and longer stays than non-GH patients.
Manuscript under submission.
Link to AUA NCS abstract (Podium #16 on pg 11)


Automated Surgical Step Recognition in Transurethral Bladder Tumor Resection Using Artificial Intelligence: Transfer Learning Across Surgical Modalities
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Abhinav Khanna
We developed an AI-based computer vision algorithm for automated surgical step recognition (SSR) in transurethral resection of bladder tumors (TURBT). The algorithm was trained on manually annotated TURBT videos and achieved an overall accuracy of 89.6% when compared to human annotations. This study represents the first application of transfer learning from laparoscopy-based computer vision models to surgical endoscopy, demonstrating the potential of this approach in adapting to new procedure types. Automated SSR in TURBT has wide-ranging applications, including quality and safety assessment, surgical education, and optimizing operating room logistics.
Predictors of Reoperation Following Primary Artificial Urinary Sphincter Placement in a Large Institutional Database
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Brian Linder
In this study, we analyzed data from patients who underwent artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) placement for post-prostatectomy incontinence to identify predictors of re-surgery for device failure. Multivariable analyses revealed that prior radiation therapy and anticoagulant use were associated with the risk of all-cause reoperation, while older age and radiation therapy were associated with device infection/erosion. Patient age and anticoagulant use were also associated with the risk of device malfunction. These findings emphasize the importance of individualized patient counseling regarding AUS device survival based on specific clinical factors.
First Author manuscript under works
Impact of Hypogonadism in Radical Cystectomy
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Abhinav Khanna
In this study we investigated the impact of pre-operative testosterone levels on outcomes following radical cystectomy for urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Patients with pre-operative hypogonadism had significantly worse overall and cancer-specific survival compared to eugonadal patients, highlighting the need for further research on the role of testosterone in the peri-operative setting.
Prospective study in planning.
Impct of Obesity on Prostatectomy Outcomes: Insights from. Large Prospectivel Maintained Cohort
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Vidit Sharma
We investigated the impact of BMI on outcomes in 21,604 patients who underwent radical prostatectomy. Obese patients had higher rates of positive surgical margins, early complications, and technical challenges. Higher BMI was associated with lower odds of recovering potency but not with continence. Patients with BMI<20 and BMI>30 had higher non-prostate cancer mortality, but similar oncologic outcomes. Our findings suggest that radical prostatectomy in obese patients can be challenging but delivers similar oncologic results, which is useful for patient counseling.
Manuscript under submission
Impct of Prostate Size on Prostatectomy Outcomes
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Vidit Sharma
We studied the association between prostate size and outcomes after radical prostatectomy in 19,160 patients. Larger prostates had higher PSAs, lower incidence of positive margins, and lower rates of post-operative potency and continence. Multivariable analysis showed that increasing prostate size was associated with lower risk of positive margins, reduced biochemical recurrence, and increased risk of incontinence, but not with post-operative impotence. These findings suggest that larger prostates may form less aggressive cancers and can inform surgical counseling. Further research is needed to understand the biological basis of this observation.
National Trends of Inpatient Urologic Oncology Procedures through the Initial COVID-19 Pandemic
Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
PI: Dr Vidit Sharma
We investigated trends in urologic oncology surgical volume during the COVID-19 pandemic using the National Inpatient Sample. Following the pandemic's onset in March 2020, there were significant decreases in monthly volumes for radical prostatectomy (49%), radical nephrectomy (32%), and partial nephrectomy (56%), but not for radical cystectomy. Surgical volumes recovered within 3-6 months, but without a compensatory increase for deferred cases. Estimated lost surgeries ranged from 19.2% for partial nephrectomy to 6.9% for radical cystectomy. Our findings suggest that some patients may have never received their indicated surgery due to the pandemic.
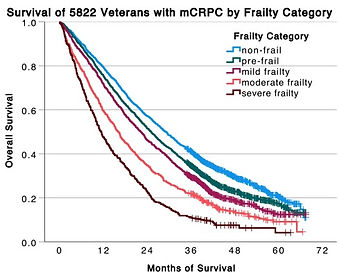
Frailty and survival among veterans treated with abiraterone or enzalutamide for mCRPC
Saint Louis University School of Medicine
PI: Dr Martin Schoen
We conducted a retrospective study of 5,822 US veterans treated with abiraterone or enzalutamide for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). Frailty was assessed using the Veterans Affairs Frailty Index (VA-FI), with patients categorized as frail if VA-FI scores were > 0.2. Frail patients (39.7%) were older and had shorter overall survival (OS) compared to non-frail patients. Among non-frail patients, there was no significant difference in OS between abiraterone and enzalutamide treatment. However, frail patients and those with dementia treated with enzalutamide had improved OS compared to those treated with abiraterone. These findings suggest that frailty and comorbidities may influence the efficacy of mCRPC treatments, highlighting the need for personalized therapy selection among frail adults.
Link to First Author publication
Association of Male Hypogonadism With Risk of Hospitalization for COVID-19
Saint Louis University School of Medicine
PI: Dr Sandeep Dhindsa
This cohort study investigated COVID-19 hospitalization rates among 723 men with hypogonadism, eugonadism, or those receiving testosterone therapy (TTh). Men with hypogonadism had a higher likelihood of being hospitalized with COVID-19 compared to men with eugonadism, even after adjusting for age, BMI, race/ethnicity, immunosuppression, and comorbidities. Men receiving TTh had a similar risk of hospitalization as men with eugonadism. However, men receiving inadequate TTh (subnormal testosterone levels while on TTh) had higher odds of hospitalization compared to men with normal testosterone levels while on TTh. These findings suggest that screening and appropriate treatment for hypogonadism may be a strategy to prevent severe COVID-19 outcomes in men.
Exploring the link between ACEs and opioid use: A systematic review
Saint Louis University School of Medicine
PI: Dr Dixie Meyer
This systematic review of 48 articles found that increased frequency of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) is directly related to an increased risk of opioid use disorder (OUD), lower onset age, and greater OUD severity. The review recommends that medical professionals target children experiencing multiple ACEs for preventative intervention, include ACEs in opioid misuse risk assessments, and foster resilience early in life. Future research should focus on interventions interrupting the progression of ACEs to OUD and explore proposed biochemical pathways.
Link to First Author publication
Testicular Cancer and Paraneoplastic Encephalitis: A Review of the Current Literature
Saint Louis University School of Medicine
PI: Dr Zachary Hamilton
This systematic review of 29 articles found that paraneoplastic encephalitis (PE) symptoms can manifest at any stage of testicular cancer (TC) and that microscopic testicular tumors are often overlooked, leading to diagnostic delays. The review emphasizes the importance of early recognition and appropriate diagnostic workup, including consideration for microscopic neoplasms, for timely intervention and improved outcomes in TC patients with neuro-psychiatric symptoms.
How Agent Orange impacts prostate cancer risk, pathology, and treatment outcomes
Saint Louis University School of Medicine
PI: Dr Zachary Hamilton
In our review, we analyzed the impact of Agent Orange (AO) exposure on prostate cancer (PC) among veterans. We conducted a comprehensive literature search and reviewed 13 relevant studies from 108 identified. The results were mixed and generally conflicting regarding PC incidence, age at diagnosis, and severity in AO-exposed veterans. Our findings indicate no significant differences in survivorship, suggesting that clinicians should base PC screening and treatment decisions on individual case evaluations.
Validation of the ALONE Scale: A Clinical Measure of Loneliness
Saint Louis University School of Medicine
PI: Dr John E Morley
This cross-sectional study examined the validity and reliability of the ALONE scale, a rapid loneliness screening tool for older adults. The ALONE scale showed strong correlation with the UCLA-20 Loneliness Questionnaire among ambulatory clinic participants (n=199) and fair correlation among nursing home patients (n=22). The scale demonstrated strong test-retest reliability and performed well across demographic subgroups. ROC curve analysis determined ALONE scale scores of 8 and greater as optimal for severe loneliness screening. The brief and comprehensible nature of the ALONE scale makes it suitable for use in clinical settings to assess older adults for severe loneliness.
Link to First Author publication
Validation of the Saint Louis University Quality of Life Questionnaire in Older Adults with Alzheimer’s Disease
Saint Louis University School of Medicine
PI: Dr John E Morley
This prospective validation study investigated the validity of LIFEAD, a brief 6-item quality of life (QOL) questionnaire, compared to the QOL-AD in 285 adults aged 65 and older with mild to moderate cognitive impairment. The study validated LIFEAD as a short, practical questionnaire that can assess QOL in this population in clinical and nursing home settings, and it can be administered in approximately 1 minute.
Link to manuscript
Prognostic Value of Systemic Inflammation Indices in Radical Cystectomy: A Comprehensive Analysis of SII and NLR
Mayo Clinic Rochester
PI: Dr Abhinav Khanna
We investigated the association between pre-operative Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) with post-operative outcomes in 738 urothelial carcinoma patients undergoing radical cystectomy (RC). Higher pre-operative SII and NLR values were significantly associated with worse overall and cancer-specific survival, even after adjusting for clinical factors known to be associated with survival. However, the temporal trend of change in pre-operative SII and NLR over time was not significantly associated with post-operative outcomes. These findings suggest that pre-operative SII and NLR may have utility in pre-operative risk stratification and as potential biomarkers to guide patient selection for adjuvant systemic therapy after RC. Future prospective studies should explore their clinical utility in this context.
First Author manuscript under works.
Using Artificial Intelligence to Characterize Body Composition in Patients Undergoing Cytoreductive Nephrectomy
Mayo Clinic Rochester
PI: Dr Vidit Sharma
We developed an AI algorithm to characterize body composition in 185 patients undergoing cytoreductive nephrectomy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. The algorithm identified a high proportion of patients with unfavorable body composition metrics, such as sarcopenia and high visceral to subcutaneous fat ratio. Although these metrics were not associated with overall survival or complications in this study, further research is needed to determine if AI-identified body composition can improve patient selection for this surgery.
National Trends in Same Day Discharge for Radical Prostatectomy: An Evolution in Practice Patterns
Mayo Clinic Rochester
PI: Dr Vidit Sharma
We analyzed national trends in same-day discharge (SDD) for radical prostatectomy (RP) using the National Inpatient Survey database from 2016-2020. The rate of SDD increased from 0.6% in 2016 to 3.5% in 2020, primarily driven by hospitals with the highest annual caseloads. SDD was associated with a $5,349 reduction in hospital charges. Minimally invasive surgical approach and high annual hospital caseload were significantly associated with SDD, while larger hospital bedsize moderated the association between caseload and SDD. While the increasing trend in SDD may favorably impact hospital bed utilization, further definition of optimal care pathways is needed before widespread implementation.
Manuscript under submission
Hospital Case Volume Distribution and Outcomes for Patients Undergoing Radical Nephrectomy with IVC or Intra-Atrial Tumor Thrombus: Data from the National Inpatient Sample
Mayo Clinic Rochester
PI: Dr Vidit Sharma
This study analyzed national data on renal cell carcinoma patients undergoing radical nephrectomy (RN) with venous tumor thrombus (VTT) involvement. It found that 3.6% of RNs required significant interventions for inferior vena cava (IVC) or cardiac VTT, which were linked to higher complication rates. Most of these procedures occurred at hospitals performing fewer than ten cases per year, with better outcomes at hospitals with higher annual caseloads. The findings suggest the benefits of centralizing care for such complex surgeries to improve patient outcomes.
Manuscript under submission
Real-Time Kidney Stone Segmentation During Distinct Ureteroscopic Tasks Using a Computer Vision Model
Vanderbilt University
PI: Dr Nicholas L Kavoussi
This study developed a robust deep learning model for automated kidney stone segmentation in ureteroscopic videos, trained on a large dataset of diverse cases. The model demonstrated excellent performance across various surgical tasks and endoscopic modalities, with non-inferior segmentation accuracy compared to expert endourologists. This foundational work establishes the feasibility of real-time operative video annotation and represents a crucial step towards developing an image-guided surgical system to improve patient outcomes in ureteroscopic lithotripsy.
Manuscript under submission.

Leptomeningeal metastases in prostate cancer: A review of the current literature
Saint Louis University School of Medicine
PI: Dr Zachary Hamilton
In our study, we investigated the relationship between prostate cancer (PC) and leptomeningeal metastasis (LMC), a serious complication affecting the meninges and spinal cord. We reviewed 23 case reports and 2 retrospective studies of PC patients who developed LMC. Our findings revealed that LMC typically occurs years after PC remission and progresses rapidly. We noted that diagnosis is often delayed due to limitations in current imaging techniques. Our research showed that treatment remains largely palliative, with poor prognosis. Based on our results, we recommend increased surveillance for LMC in high-risk PC patients, particularly those with high-grade or hormonal PC.
Leptomeningeal metastases in prostate cancer: A review of the current literature
Saint Louis University School of Medicine
PI: Dr Zachary Hamilton
In our study, we examined the treatment patterns for upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) in the inpatient setting. We analyzed five years of national data. Our findings revealed that 90% of inpatient surgical treatments for UTUC were extirpative, while 10% were endoscopic. Patients undergoing endoscopic treatment tended to be older and have more comorbidities. Although endoscopic procedures had lower median inpatient charges, they were associated with a higher likelihood of complications. Despite this, endoscopic treatments showed similar lengths of stay compared to extirpative surgeries. Our results support the use of endoscopic management for UTUC in patients who may not be suitable candidates for nephroureterectomy, particularly older patients with higher comorbidity scores.
Characterization of Surgical Inpatient Care for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma
Vanderbilt University
PI: Dr Nicholas L Kavoussi
In our study, we examined the treatment patterns for upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) in the inpatient setting. We analyzed five years of national data. Our findings revealed that 90% of inpatient surgical treatments for UTUC were extirpative, while 10% were endoscopic. Patients undergoing endoscopic treatment tended to be older and have more comorbidities. Although endoscopic procedures had lower median inpatient charges, they were associated with a higher likelihood of complications. Despite this, endoscopic treatments showed similar lengths of stay compared to extirpative surgeries. Our results support the use of endoscopic management for UTUC in patients who may not be suitable candidates for nephroureterectomy, particularly older patients with higher comorbidity scores.
PSMA-PET Guided Metastasis Directed Therapy for Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer
Mayo Clinic
PI: Dr RJ Karnes
In our study, we investigated the utility of PSMA-PET scans in improving diagnostics and therapeutics for oligometastatic prostate cancer (OM PCa). We reviewed PSMA-PET scans performed at our institution over a seven-month period, identifying 141 patients with oligometastatic disease. Our findings showed that the majority of metastases were osseous (63.8%) or nodal (43.3%), with an average of 2.14 metastatic sites per patient. Treatment modalities varied, with stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) being the most common (49.6%), followed by androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) (57.4%). On follow-up imaging, 48.5% of cases resolved, and 32.38% improved. Notably, our multivariable analysis revealed that metastasis-directed therapy combined with ADT significantly predicted both radiographic and biochemical progression-free survival. Based on these results, we conclude that PSMA-PET is an excellent tool for diagnosing and guiding the management of oligometastatic prostate cancer.
PSMA-PET for Initial Biochemical Recurrence After Radical Prostatectomy
Mayo Clinic
PI: Dr RJ Karnes
In our study, we investigated the efficacy of PSMA-PET-CT in detecting biochemically recurrent (BCR) prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. We found a detection rate of 60.5% for PSMA PET-CT, significantly outperforming conventional imaging. The most common recurrence patterns were regional node involvement (31.4%) and local recurrence (21.6%). Our analysis revealed that PSMA-PET-CT led to various management strategies, including salvage radiation and androgen deprivation therapy. Notably, pathologic N1 stage and positive surgical margins were identified as significant predictors of lesion detection on PSMA-PET. These findings suggest that PSMA-PET-CT is a valuable tool for guiding management in patients with biochemically recurrent prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy.
Automated Renal Volume Measurement Using Artificial Intelligence: Correlation to Post-Operative Renal Function After Radical and Partial Nephrectomy
Mayo Clinic
PI: Dr Abhinav Khanna
In our study, we developed a novel deep learning algorithm to automatically measure renal volume from CT images, aiming to predict post-operative renal function (PORF) after radical and partial nephrectomies. We analyzed CT images from 1,077 patients and found that higher AI-derived contralateral renal volume was independently associated with better PORF in both types of surgeries. Specifically, each 10% increase in split contralateral renal volume corresponded to a 6.5 and 2.6 mL/min/1.73 m2 increase in PORF following radical and partial nephrectomies, respectively. These associations remained significant even after adjusting for known clinical factors. Our AI tool automates the measurement of non-neoplastic renal volume, potentially facilitating its integration into clinical practice for improved prediction of post-operative renal function.
Patient Selection for Upfront Cytoreductive Nephrectomy: Assessment of Two Clinical Risk Stratification Tools
Mayo Clinic
PI: Dr Vidit Sharma
In our study, we evaluated the predictive accuracy of two prognostic tools for cytoreductive nephrectomy (CN): the Selection for Cytoreductive Nephrectomy (SCREEN) score and the Leibovich metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) score. We analyzed data from 248 patients who underwent upfront CN for metastatic RCC between 2005 and 2021. Our results showed that both scoring systems could predict overall survival, with the SCREEN score demonstrating median survival times of 3.9, 2.1, and 1.6 years for favorable, intermediate, and poor risk groups, respectively. The Leibovich score also showed increased risk of death for higher risk groups. However, both tools demonstrated only modest discriminative accuracy, with c-indices of 0.57 for SCREEN and 0.66 for Leibovich. We conclude that while these tools are useful for prognostication, there is a need for more advanced risk stratification methods, such as radiomics, tumor sequencing, or biopsy of metastatic sites, to improve decision-making for CN.
Practice Trends of Early Career Urologic Oncologists
Mayo Clinic
PI: Dr Vidit Sharma
In our study, we analyzed the practice patterns of early career urologic oncologists using American Board of Urology (ABU) case logs from 130 fellowship-trained graduates between 2012 and 2020. We found that the median number of cases performed in the first year of practice was 171, with oncology cases being the most common. Interestingly, there were no significant differences in case load between male and female surgeons. However, urologists in private practice performed more cases overall, including more general, men's health, endourology, and urogynecologic procedures. Notably, the number of oncologic cases remained consistent across both academic and private practice settings. The most common oncologic procedures were prostate needle biopsies, followed by transurethral resection of bladder tumors. Our findings provide valuable insights into the expectations for those considering a career in urologic oncology, highlighting that nearly half of the cases performed are in general urology and endourology, with variations depending on the type of practice.
Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Nephrectomy Following Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: Data from a Multicenter Study
University of Southern California
PI: Dr Hooman Djaladat
In our study, we investigated the outcomes of minimally invasive surgery (MIS) nephrectomy following immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). We analyzed data from 158 patients across five high-volume U.S. academic centers between 2015 and 2023. Our findings showed that 76 patients underwent MIS nephrectomy, with a conversion rate to open surgery of 8%. Multivariable analysis revealed that patients with non-metastatic RCC, smaller tumor size, and no evidence of inferior vena cava thrombus were more likely to undergo MIS. The 90-day complication rate for MIS nephrectomies was 22%, with 8% being Clavien grade 3 or higher. Importantly, there was no 90-day mortality reported. These results suggest that minimally invasive nephrectomy can be safely performed in carefully selected patients with advanced RCC who have received ICI therapy.
Leveraging Mixed-Reality for the Remote Delivery of Care to Developing Nations
Mayo Clinic
PI: Dr Swaiman Singh
Medical professionals have a deep desire to help during humanitarian crises, but flying to remote destinations can be prohibitive due to associated travelling costs, and personal and professional obligations. We are working on a project to explore the use of mixed reality to enable physicians to provide remote care in areas of disaster through the lens’ of ground personnel
Additionally mentoring several undergraduate students to help them in developing survey-based research projects focused on global health.
Abstract presented at NASMDA 2024
Re-engineering Biopsy to Improve Bladder Cancer Staging
Mayo Clinic
PI: Dr Vidit Sharma
Ongoing Study. Helped PI Vidit Sharma secure $131,085 over 2 years to conduct study.
HRQOL in Partial Cystectomy
Mayo Clinic
PI: Dr Vidit Sharma
Helped PI Vidit Sharma secure $8,531.90 in funding to study HRQOL in Partial Cystectomy patients.
Previously I have also helped write a publication (currently under submission) to compare oncologic outcomes in partial cystectomy to radical cystectomy patients.
Continued improvements to Body Composition Algorithms
Mayo Clinic
PI: Dr Vidit Sharma
Helped secure $5,571.80 in funding for work on an improved algorithm for longitudinal AI derived body composition analysis in cystectomy, nephrectomy, and advanced prostate cancer patients
Survey about Urologist Opinions on Sharing Surgical Video
Mayo Clinic
PI: Dr Abhinav Khanna
In this study, we are conducting a cross-sectional survey of 5000 practicing urologists in the United States to explore their opinions on sharing anonymized surgical video recordings. We are assessing their attitudes, identifying concerns, and determining the conditions under which they are willing to share surgical video data. Through this research, we aim to contribute valuable insights to the ongoing discussion about the ethical and practical implications of digital technologies in urology and surgery at large.